Thank you for your support :)
CC BY 4.0 (Attribution 4.0 International)
Leetcode 935.Knight Dialer
The chess knight has a unique movement, it may move two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically (with both forming the shape of an L). The possible movements of chess knight are shown in this diagaram:
A chess knight can move as indicated in the chess diagram below:
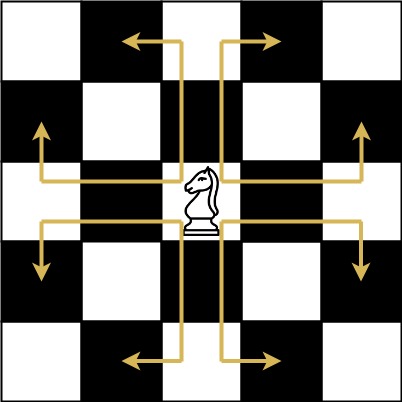
We have a chess knight and a phone pad as shown below, the knight can only stand on a numeric cell (i.e. blue cell).
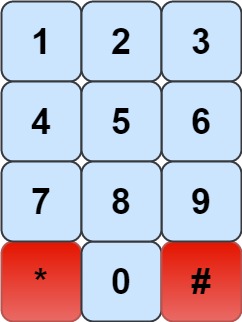
Given an integer n, return how many distinct phone numbers of length n we can dial.
You are allowed to place the knight on any numeric cell initially and then you should perform n - 1 jumps to dial a number of length n. All jumps should be valid knight jumps.
As the answer may be very large, return the answer modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1
Output: 10
Explanation: We need to dial a number of length 1, so placing the knight over any numeric cell of the 10 cells is sufficient.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2
Output: 20
Explanation: All the valid number we can dial are [04, 06, 16, 18, 27, 29, 34, 38, 40, 43, 49, 60, 61, 67, 72, 76, 81, 83, 92, 94]
Example 3:
Input: n = 3
Output: 46
Example 4:
Input: n = 4
Output: 104
Example 5:
Input: n = 3131
Output: 136006598
Explanation: Please take care of the mod.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 5000
Solution 1: DFS + memoization
public class Knight_Dialer_DFS {
// Time O(10 * N) = O(N)
public int knightDial(int N) {
int count = 0; // count the result
int[][] memo = new int[N][10]; // memoization
for (int pos = 0; pos < 10; pos++) {
memo[0][pos] = 1; // initialize the memo
}
for (int pos = 0; pos < 10; pos++) {
count += knightDial(pos, N - 1, memo);
}
return count;
}
private int knightDial(int pos, int hops, int[][] memo) {
if (memo[hops][pos] != 0) {
return memo[hops][pos];
}
int count = 0;
for (int next: neighbors[pos]) {
count += knightDial(next, hops - 1, memo);
}
memo[hops][pos] = count;
return count;
}
//private final int[][] neighbors = {4, 6}, {6, 8}, {7, 9}, {4, 8}, {0, 3, 9}, {}, {0, 1, 7}, {2, 6}, {1, 3}, {2, 4};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Knight_Dialer_DFS solution = new Knight_Dialer_DFS();
// test case
int a = solution.knightDial(10);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|
| O(10 * N) = O(N) | O(10 * N) = O(N) |
| 利用了memoization后,recursion 对0~9每个position调用DFS function,每个position对应的hops数只需要记录一遍,用memoization存下来 | In place的操作,不需要额外matintain空间 |
Solution 2: DP
public class Knight_Dialer_DP {
public int knightDial(int N) {
// memo[hops][pos] represents the number of solutions ending at pos in hops
int[][] memo = new int[N][10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
memo[0][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
for (int next: neighbors[j]) {
memo[i][j] += memo[i - 1][next];
memo[i][j] %= Math.pow(10, 9) + 7; // 防止stack overflow
}
}
}
int sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) {
sum += memo[N - 1][k];
}
return (int)(sum % (Math.pow(10, 9) + 7));
}
// private final int[][] neighbors = {4, 6}, {6, 8}, {7, 9}, {4, 8}, {0, 3, 9}, {}, {0, 1, 7}, {2, 6}, {1, 3}, {2, 4};
public static void main(String[] args) {
DP.Knight_Dialer_DP solution = new DP.Knight_Dialer_DP();
// test case
int a = solution.knightDial(10);
System.out.println(a);
}
| Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|---|
| O(10 * N * 3) = O(N) | O(10 * N) = O(N) |
| DP的方法利用三层循环,其中第三层只是generate邻居,最多只有3个 | 只需要maintain一个10 * N的memoization |
